Knockin Cell Line
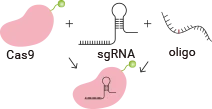
The gRNA vector (containing Cas9) of the CRISPR/Cas9 system and the Donor vector carrying the target mutation or target gene sequences will be co-transfected into cells via electroporation. Subsequently, the gRNA-Cas9 complex will induce a double-strand break (DSB) at the target site on the DNA. The cells will then undergo homologous recombination repair (HDR), using the Donor vector as a template to integrate the target mutations into the target sites. After antibiotic selection, single-cell clones will be generated. Positive clones that have successfully incorporated the target mutations will be validated through amplification and sequencing of the target sites. The final deliverables will include the validated positive cell clones, related experimental data, and project reports.
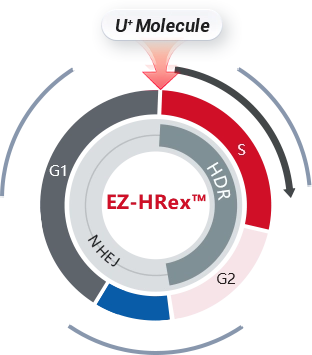
EZ-HRex™ New Technique
After years of R&D of Ubigene, based on the original CRISPR-U™ gene-editing technique, Ubigene has upgraded it to EZ-HRex™ New Technique, by innovatively adding U+ Molecule.
Effectively regular cell cycles, promoting more post-transfection cells into S/G2 phases.
Reduce the NHEJ pathway activity, reducing the proportion of indel genotype to improve the HDR efficiency.
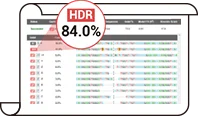
By reducing the activity of the NHEJ pathway, the proportion of indel genotypes is decreased, thereby enhancing HDR efficiency. Following optimization, the HDR efficiency for gene mutation and fragment knock-in in cells has been significantly improved across the board. At the post-transfection cell pool level, the proportion of HDR genotypes can reach up to 84% .
By reducing the activity of the NHEJ pathway, the proportion of indel genotypes is decreased, thereby enhancing HDR efficiency. Following optimization, the HDR efficiency for gene mutation and fragment knock-in in cells has been significantly improved across the board. At the post-transfection cell pool level, the proportion of HDR genotypes can reach up to 84% .
Knockin (KI) Cell Service
Cell type
Various types of cells including tumor cell lines, regular cell
Service type
RNP Method, Prime Editor, Base Editing, Antibiotics-based Konck
Deliverables
Single-cell clone
Turnaround/Price
8 weeks, as low as $6480
Digestive System
Endocrine System
Respiratory System
Reproductive System
Circulatory System
Blood and lymphatic System
Brain and Nervous System
Urinary System
Skeleton, Articulus, Soft Tissue, Derma System
Stem Cell Lines
Ocular, Otolaryngologic and Oral System

Point Mutation (PM) Cells Construction Methods
4 solutions to meet different mutation needs!
Incubate sgRNA and Cas9 protein in vitro to form an RNP (ribonucleoprotein) complex, which is then co-transfected into cells along with a single-stranded oligonucleotide. After the RNP induces a double-strand break at the target site, the oligonucleotide can introduce the desired mutation into the genomic target through homologous recombination.
- Broad applicability
- High editing efficiency
- Short turnaround time
Features:
- Suitable when a gRNA sequence can be identified within approximately 10 bp of the mutation site.
- Applicable to target cells that can be transfected using electroporation or liposome-based transfection.
Applicable Types:
Gene editing is achieved by fusing an engineered reverse transcriptase with a Cas9 nickase and using a special prime editing guide RNA (pegRNA).
- Capable of correcting various complex mutations.
- However, it has low editing efficiency and requires complex vector design.
Features:
- Suitable for correcting complex mutations.
- Ideal for cases where an appropriate gRNA sequence cannot be found near the mutation site.
Applicable Types:
A base editing system is developed by integrating a base deaminase with the CRISPR/Cas system, enabling precise introduction of C/G-to-T/A and A/T-to-G/C point mutations without creating double-strand breaks, thereby achieving highly efficient and accurate gene editing.
- High efficiency, but applicable cases are limited.
Features:
- Suitable for specific single-base conversions (C⇌T; A⇌G) when the target site is within the active window.
Applicable Types:
The donor vector is constructed using a plasmid, with a resistance gene expression cassette inserted into an intron to enhance the efficiency of point mutation recombination through antibiotic screening.
- Suitable for scenarios where a suitable gRNA sequence cannot be identified near the mutation site; however, it is relatively expensive and has a longer experimental cycle.
Features:
- Ideal for cases where a suitable gRNA sequence cannot be identified near the mutation site.
Applicable Types:
Knockin Strategies
Protein fusion
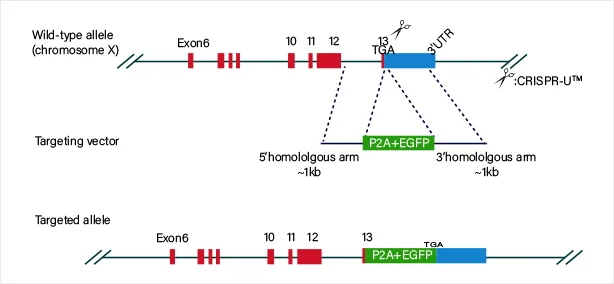
View Picture
The guide RNA and Cas9 complex induce a double-strand break (DSB) at the target site of the DNA. The donor vector carrying the knock-in sequence serves as the template for homologous recombination repair (HDR), facilitating the recombination of the knock-in sequence into the target site.
Replacement of specific locus
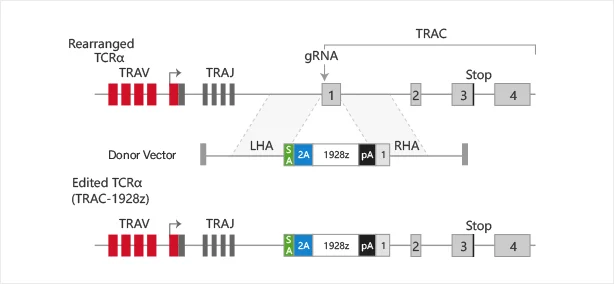
View Picture
Workflow and Validation
Strategy Design by Red Cotton System

RNP Complex
Cell Transfection

Pool Efficiency Validation
Single-cell Cloning
PCR Amplification
Sanger Sequencing Validation
QC & Cell Cryopreservaion

FAQs
1. What is CRISPR knock-in?
CRISPR knock-in refers to the process of using the CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology to insert a specific genetic sequence (such as a gene, regulatory element, or mutation) into a precise location in the genome. This technique is used to add functional genes or introduce specific genetic modifications in a targeted manner, as opposed to CRISPR knock-out, where genes are disrupted or deleted.
2. How does CRISPR Knock-in Work?
- Designing the Guide RNA (gRNA): A guide RNA is designed to specifically target a location in the genome where the new DNA sequence will be inserted. This RNA sequence is complementary to the target DNA sequence, ensuring that Cas9 cuts the correct location in the genome.
- Cas9 Protein: The Cas9 protein, which is part of the CRISPR system, is responsible for making a double-strand break at the target location in the DNA.
- Donor DNA Template: To achieve the knock-in, a donor DNA template is introduced into the cell. This template contains the genetic sequence that will be inserted into the genome. The donor template typically has homology arms (sequences that match the regions adjacent to the target break) to guide the cell's repair machinery.
- Homology-Directed Repair (HDR): After Cas9 cuts the DNA, the cell uses its HDR mechanism to repair the break. If a donor template is provided, the cell incorporates the new genetic material from the donor DNA into the genome at the break site, which results in the insertion of the desired sequence.
3. What are the differences between CRISPR gene knock-in and knock-out ?
| key Differences | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | CRISPR Knock-in | CRISPR Knock-out |
| Purpose | To insert a specific gene or sequence into the genome. | To disrupt or inactivate a gene in the genome. |
| Outcome | Addition of a gene or sequence at a specific site. | Loss-of-function mutation due to gene disruption. |
| Repair Mechanism | Homology-directed repair (HDR) using a donor template. | Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) that introduces errors at the break site. |
| Resulting Change | Insertion of new genetic material (e.g., a gene, mutation, or reporter sequence). | Gene is disrupted or inactivated, often with indels. |
| Use Cases | Gene therapy, disease modeling, synthetic biology, protein production. | Gene function studies, disease modeling, cancer research, drug discovery. |
4. What are the applications of CRISPR Knock-in?
- Gene Therapy: Knock-in CRISPR can be used to insert healthy copies of defective genes in patients with genetic disorders. For example, correcting mutations in the CFTR gene (responsible for cystic fibrosis) by inserting a functional copy into a patient's cells.
- Disease Modeling: Researchers use knock-in to introduce specific mutations into the genome of animal models (like mice or rats) to study diseases or test therapies. This helps in creating models of genetic diseases such as cancer or neurodegenerative conditions.
- Synthetic Biology: Scientists can insert new genes into organisms (bacteria, yeast, or plants) to create new functions, such as engineered microbes that produce biofuels or therapeutic proteins.
- Drug Development: In drug discovery, knock-in CRISPR is used to create cell lines or animals that express specific mutations or diseases, allowing for more accurate testing of drugs or potential treatments.
- Cell Line Engineering: For industrial or therapeutic use, CRISPR knock-in can generate cell lines that express desired proteins, enzymes, or other bioactive molecules for research or commercial purposes.
5. How to perform a CRISPR Knockin Experiment?
- Cell Type: Choose an appropriate cell line or primary cell type for your experiment.
- Efficiency: CRISPR knock-ins generally have lower efficiency than knock-outs, and larger inserts can reduce efficiency further.
- Delivery Method: Choose a delivery method (electroporation, lipid-based, viral) based on your cell type's transfection efficiency.
- Homology-directed Repair (HDR): The success of knock-ins heavily relies on HDR, which is not as efficient as non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). You can enhance HDR by using HDR enhancers or small molecules (like SCR7).
- Verification: Always validate your knock-in using multiple methods (PCR, sequencing, protein expression).
Ubigene could provide 4 solutions to meet different mutation needs! Get in touch with our experts now
6. How to validate CRISPR knockin cell?
Validating CRISPR knock-in cells involves confirming:
- Correct insertion of the desired gene at the target location (via PCR, sequencing, Southern blot).
- Expression of the inserted gene at the RNA and protein levels (via RT-PCR, Western blot, fluorescence assays).
- Functionality of the inserted gene, especially for functional knock-ins (via fluorescence or activity assays).
- Absence of off-target effects, to ensure the edit is precise (via sequencing or specific assays).
7. What are the challenges and limitations of CRISPR Knock-in?
After years of R&D of Ubigene, based on the original CRISPR-U™ gene-editing technique, Ubigene has upgraded it to EZ-HRex™ New Technique. With the new technology, the proportion of HDR genotypes can reach up to 84%. Get in touch with our experts now
- Efficiency: The efficiency of knock-in can be low, especially compared to knock-out techniques, because homology-directed repair (HDR) is less common than the alternative repair pathway, non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), which often leads to deletions or errors rather than precise insertions.
- Off-target Effects: Although CRISPR technology is highly specific, there is still the potential for off-target edits, where the CRISPR machinery cuts DNA at unintended sites, leading to unwanted genetic changes.
- Delivery: Delivering the CRISPR/Cas9 components (guide RNA, Cas9, and donor DNA) into cells, especially in vivo (in living organisms), is challenging. Efficient delivery systems are crucial for the success of CRISPR knock-in applications.
8. How to increase knock-In efficiency?
Ubigene has revolutionized gene editing with the new EZ-HRex™ technique, now enhanced with the innovative U+ Molecule. This breakthrough allows HDR genotype proportions to reach up to 84% at the post-transfection cell pool level. Additionally, Ubigene offers 4 tailored solutions to address diverse mutation requirements, ensuring maximum flexibility and precision in your experiments! Contact us now
9. How much does CRISPR Knock-in cost?
Ubigene offers global gene knock-in services, starting at just $6,480!
10. What is CRISPR point mutation?
CRISPR point mutation refers to using CRISPR/Cas9 technology to introduce a very specific, single-nucleotide change (A, T, C, or G) in the DNA sequence of a gene.
Instead of knocking out (deleting) a gene or inserting large DNA fragments (knock-in), point mutation precisely changes just one base pair. Scientists often use this to:
- Correct disease-causing mutations
- Create specific disease models
- Study the function of a particular amino acid in a protein
This is usually achieved by combining CRISPR/Cas9 with a carefully designed donor template (a short DNA sequence with the desired mutation) that the cell uses during repair.
11. What are the 4 types of point mutations?
- Substitution:
One base is replaced by another.
e.g. A changes to G. - Insertion:
One extra base is inserted into the DNA sequence.
e.g. An extra A is added between two bases. - Deletion:
One base is removed from the DNA sequence.
e.g. A single missing C. - Frameshift mutation (special case of insertion or deletion):
When an insertion or deletion changes the reading frame of the gene.
This can dramatically alter the resulting protein.
12. Are point mutations reversible?
Yes, especially with modern genetic technologies! Contact us now
There are 2 main lab strategies:
- CRISPR knock-in: Introduce a donor template with the correct base.
- Base editors: Use engineered CRISPR systems that can directly change one base to another without making a DNA break..
13. What are the applications of CRISPR point mutation?
- Disease modeling
- Gene function research
- Therapeutic correction
- Drug discovery and screening
- Agriculture and biotechnology
Representative publications
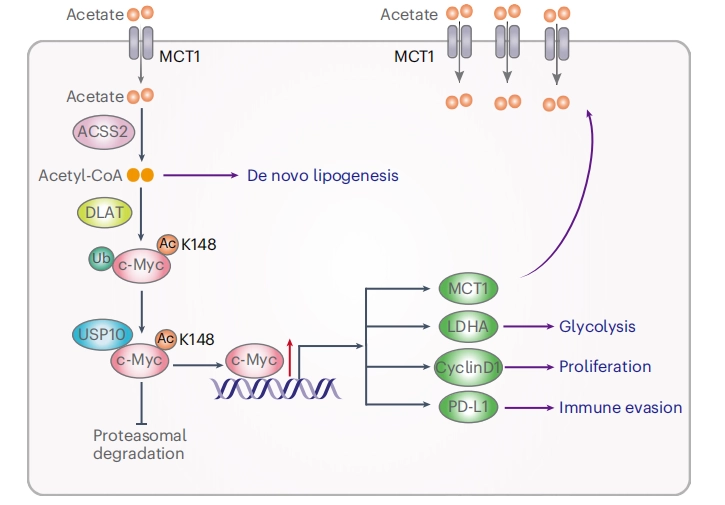
A549 Cell MYC Gene - Lung Cancer
IF=20.8
Nature Metabolism
Acetate reprogrammes tumour metabolism and promotes PD-L1 expression and immune evasion by upregulating c-Myc
This study demonstrated that acetate is the most abundant short-chain fatty acid in human non-small cell lung cancer tissue, with increased acetate uptake as the tumors enriched. The study used Ubigene-constructed MYC (p.K148R) point mutant A549 cells and MYC (p.K148Q) point mutant A549 cells, simulating acetylated and non-acetylated c-Myc states, and investigated the impact of these changes on tumor cell behavior. View details
View Picture
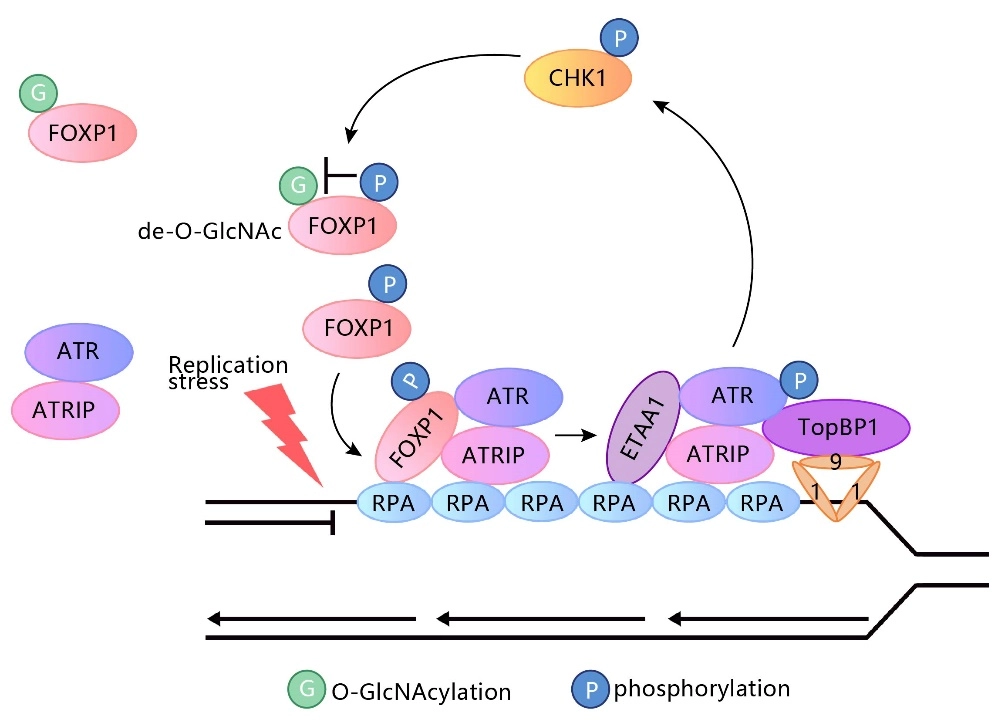
FOXP1 gene in HEK293 cells - Tumor occurrence
IF=9.4
The EMBO Journal
FOXP1 phosphorylation antagonizes its O-GlcNAcylation in regulating ATR activation in response to replication stress
This study reveals a new mechanism by which the forkhead box (FOX) transcription factor FOXP1 promotes ATR-CHK1 activation under replication stress. This function does not rely on the transcriptional regulatory activity of FOXP1 but is instead co-regulated by its phosphorylation and glycosylation modifications. The study used the source cell lines from Genewell to construct the FOXP1 gene S396A and S396D point mutation HEK293 cell lines.
View Picture