Research Value of Gene Knockout
Gene knockout cell lines are among the most widely used and reliable functional research models in modern biomedical research. By simulating the permanent loss of a gene, they allow precise assessment of how specific genes regulate cellular behaviors, thereby revealing key mechanisms underlying disease development and progression. They are widely applied in:
- Gene function annotation and the study of signaling pathways.
- Construct disease models, such as cancer, metabolic disorders, and immune-related diseases.
- Drug target screening and validation.
- Study antibody-dependent therapeutic mechanisms.
- Find 8000+ Ready-to-Use KO Cell Lines→


CRISPR-U™ Technique
CRISPR-U™ is Ubigene's proprietary CRISPR/Cas9-based platform, designed for efficient and precise gene editing in cell lines. It combines a unique gRNA design algorithm tailored to genomic features, optimized editing parameters for thousands of cell lines, accurate assessment of cell pool editing efficiency, enhanced single-clone formation techniques, and high-throughput genotyping of small cell populations. Compared to traditional methods, CRISPR-U™ can boost gene-editing efficiency by 10-20×, delivering faster and more reliable results for your research.
Exclusive innovative technique, Gene-editing efficiency improved by 10-20 times
Fast and precise identification, Saving 4 weeks to screen positive clones
300+ Success gene-editing cell lines, 8000+ Success cases
Gene Knockout Cell Service
Cell Line Type
Tumor Cells, Immortalized Cell Lines, Various cell types, including iPS and ES cells
Turnaround
Speedy turnaround as fast as 4 weeks!
Service Type
Single / Multiple Genes Knockout
Recent Special Deal
Start from $990
Deliverables
1. Cell Pool / Single-Cell Clone 2. Wild-Type Cells 3. Experimental Reports
Quality Control (QC)
1. PCR Testing (Standard) 2. Sanger Sequencing (Standard) 3. Custom Services (Tailored to Experimental Needs)
Digestive System
Endocrine System
Respiratory System
Reproductive System
Circulatory System
Blood and lymphatic System
Brain and Nervous System
Urinary System
Skeleton, Articulus, Soft Tissue, Derma System
Stem Cell Lines
Ocular, Otolaryngologic and Oral System
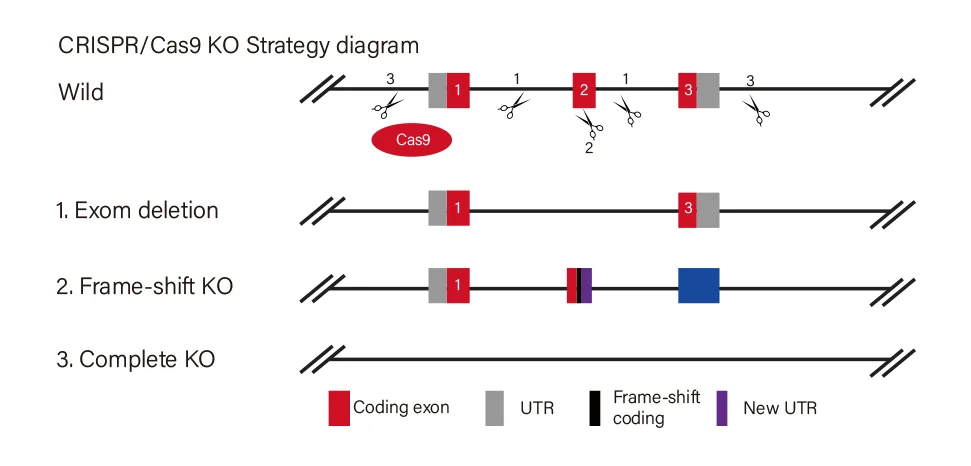
Gene Knockout Strategies
Ubigene Offers 3 Standard Gene Knockout Strategies, Customizable to Your Research Goals
Knockout Type
Target Site Design
Effect
View Picture
Workflow and Validation
Project Evaluation & Strategy Design by Red Cotton System
Understand research goals and recommend the most suitable knockout strategy and cell type.

RNP Complex Preparation
Synthesize sgRNA and prepare Cas9 protein.
Cell Transfection
Deliver RNPs into cells using electroporation platforms (e.g., Nucleofector), optimizing parameters to maximize cell viability and editing efficiency.

Cell Pool Efficiency Verification
Assess transfection and cleavage efficiency in the cell pool.

Single-Clonal Screening
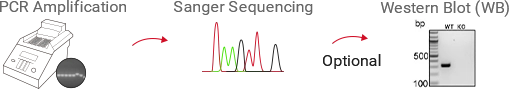
Validation & Quality Control
PCR+ Sanger sequencing + optional protein-level verification (e.g., Western Blot).
Final Deliverables
Project strategy + homozygous knockout cell lines + wild-type cells + experimental report.


Off-the-shelf KO Cell Line
8000+ in stock | From 990 USD | Deliver in 1 week
FAQs
1. How long does CRISPR gene knockout take?
Typical Timeline for CRISPR Gene Knockout
The timeline for a CRISPR gene knockout can vary depending on the organism and specific experimental setup, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months. Here’s a general breakdown of the process:
- gRNA Design and Plasmid Construction (1–2 weeks)
- Cell Line Transfection & Pool Screening (2–3 weeks)
- Single-Cell Cloning (2–4 weeks)
- Clone Validation (2–3 weeks)
With 12 years of expertise in gene editing, Ubigene expert team has optimized the entire workflow, reducing the KO cell generation timeline to as fast as 4 weeks — significantly accelerating your research progress. Connect with Ubigene's experts now to customize your exclusive KO cell line!
You may also like:
2. What are the difference between KO cells and Knockdown cells?
| Feature | Knockout (KO) | Knockdown (KD) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | CRISPR, ZFNs, TALENs (genome editing) | RNAi (siRNA, shRNA) |
| Effect on Gene Expression | Complete loss | Partial reduction |
| Permanence | Permanent | Usually transient (shRNA can be stable) |
| Protein Production | No protein produced | Reduced protein levels |
| Suitability | Studying complete gene loss, long-term studies | Studying gene function, short-term studies, essential genes |
| Best For | Disease models, drug discovery, functional genomics | Quick functional validation, gene pathway studies |
3. Is gene knockout permanent?
Gene knockout (KO) is typically permanent, especially when using genome-editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9. Here's why:
- Mechanism: In gene knockout, a DNA double-strand break is introduced at a specific location in the gene. This break is repaired by the cell’s own repair mechanisms, which often result in insertions or deletions (indels) and introduce an early stop codon,that disrupt the gene's coding sequence, causing it to lose its function. These mutations are passed on to daughter cells when they divide.
- Permanent in Cell Lines: If you're generating a knockout in a cell line, the knockout is usually stable over time, as the altered DNA will be present in every cell, and the mutation is passed down with cell division. You can even create clonal populations where all cells carry the same knockout mutation.
- Permanent in Organisms: If you're creating a knockout in an organism (such as mice or other model organisms), the gene disruption will be passed on through heredity if the knockout is done in germline cells (e.g., sperm or eggs), leading to permanent knockouts in offspring. In some cases, you might generate heterozygous knockouts first, and then breed them to produce homozygous knockouts for more complete disruption.
4. What is the purpose of a gene knockout?
The purpose of a gene knockout (KO) is to study the function of a specific gene by completely eliminating its expression or disrupting its function. By knocking out a gene, researchers can observe how the organism or cell behaves in the absence of that gene's product (usually the protein it encodes). This helps answer key biological questions and has a wide range of applications
5. How to confirm gene knockout?
- Molecular Confirmation Methods:
- PCR and Gel Electrophoresis
- Sequencing
- Southern Blotting
- Western Blotting (Protein Level Confirmation)
- qRT-PCR (Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR)
- Functional Assays:
- Phenotypic Analysis
- Reporter Genes
- Flow Cytometry (for Knockout Cells)
- Knockout Mouse/Model Organism Specific Verification:
- Breeding and Genotyping (for Mice or Other Organisms)
- Histological Analysis
6. What are the methods used to validate a knockout (KO) cell lines?
Ubigene performs genotypic validation of knockout (KO) cell lines using PCR amplification combined with Sanger sequencing to confirm successful gene disruption at the DNA level. For customers requiring additional verification, customized assays are available as supplementary services. These may include Western blotting or qPCR, depending on the target gene and specific experimental requirements.
7. Have Ubigene's KO cell lines undergone Mycoplasma testing and STR authentication?
Ubigene implements stringent quality control measures for every knockout (KO) cell line. All in-stock KO cell lines undergo comprehensive quality assurance testing prior to shipment. Each cell line is confirmed to be free from Mycoplasma contamination and authenticated by short tandem repeat (STR) profiling to verify its genetic identity and ensure authenticity.
Upon delivery, Ubigene provides a complete documentation package that includes the Mycoplasma testing report, STR authentication report, and detailed cell culture instructions. All KO cell lines are guaranteed to be contamination-free, viable, and ready for downstream experimental applications. In addition, Ubigene offers complimentary technical support and culture guidance to help customers achieve optimal cell performance and experimental outcomes.
8. Are the KO cell lines delivered by Ubigene single-cell clones or KO cell pools?
Ubigene provides two vials of a validated homozygous knockout (KO) single-cell clone (1 × 10⁶ cells per vial) as the standard deliverable. Each KO clone is isolated from a single cell to ensure genetic homogeneity and stable knockout efficiency.
However, if a KO cell pool is more suitable for your experimental design, Ubigene can also customize and deliver a KO cell pool upon request.
9. How should I store the KO cells (cryopreserved cells) upon receipt?
Upon receipt, Ubigene’s KO cells are delivered as cryopreserved vials. To maintain cell viability and ensure optimal experimental performance, please follow the storage and handling guidelines below:
- Immediate storage: Upon arrival, promptly transfer the vials into liquid nitrogen (LN₂) for long-term storage. This ensures maximal preservation of cell viability and genetic stability.
- Short-term storage: If liquid nitrogen storage is not immediately available, the vials may be temporarily stored at −80 °C for up to several days. Avoid prolonged storage at −80 °C and prevent any freeze–thaw cycles, as they may significantly reduce cell viability.
- Thawing and recovery: Ubigene provides a detailed Cell Use Instruction with each shipment. Please follow the recommended thawing and culture procedures carefully to ensure optimal cell recovery and growth.
Note: Always handle cryopreserved cells under aseptic conditions and minimize exposure to ambient temperature during transfer. Proper storage and handling are critical to maintaining cell viability, genetic integrity, and experimental reproducibility.
Contact us for more information10. What should I do if I encounter any issues after thawing the cells or face other technical problems?
Don't worry — Ubigene provides 24/7 technical support to assist you with any challenges you may encounter during cell recovery or subsequent experiments. If you experience any issues, simply leave us a message or contact our technical support team. Our specialists will review your case and provide professional guidance within 24 hours of receiving your inquiry.
Contact us for more informationUbigene is committed to ensuring the success of your experiments. From cell thawing and culture optimization to troubleshooting and data interpretation, our technical experts are here to provide timely, personalized assistance every step of the way.
Representative publications
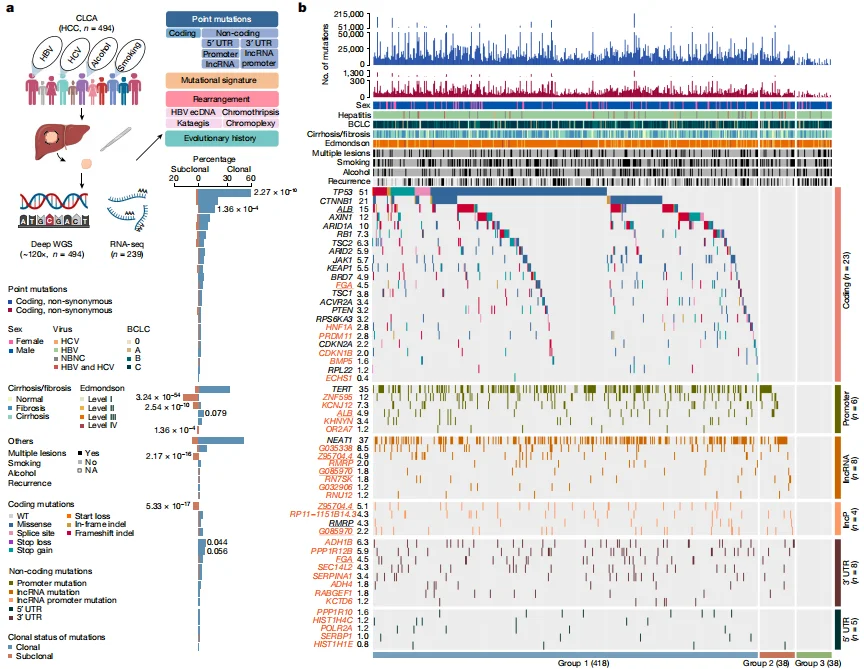
PPP1R12B/KCNJ12/FGA knockout Hep G2 cell line-liver tumors
IF=64.8
Nature
Deep whole-genome analysis of 494 hepatocellular carcinomas
This study completed the Chinese Liver Cancer Atlas (CLCA) and three newly identified potential driver events were also selected for detailed functional verification. It was found that mutations in the above genes were sufficient to cause significant changes in gene expression levels (Among them, PPP1R12B, KCNJ12, FGA knockout cells and overexpression lentiviruses carrying mutations were all constructed by Ubigene), and were involved in regulating various malignant phenotypes of hepatocellular carcinoma, These results confirm the validity of the new driving events found based on data analysis. View details
View Picture
STING1 Knockout in HeLa cell line——prevention and treatment of viral diseases
IF=32.4
Immunity
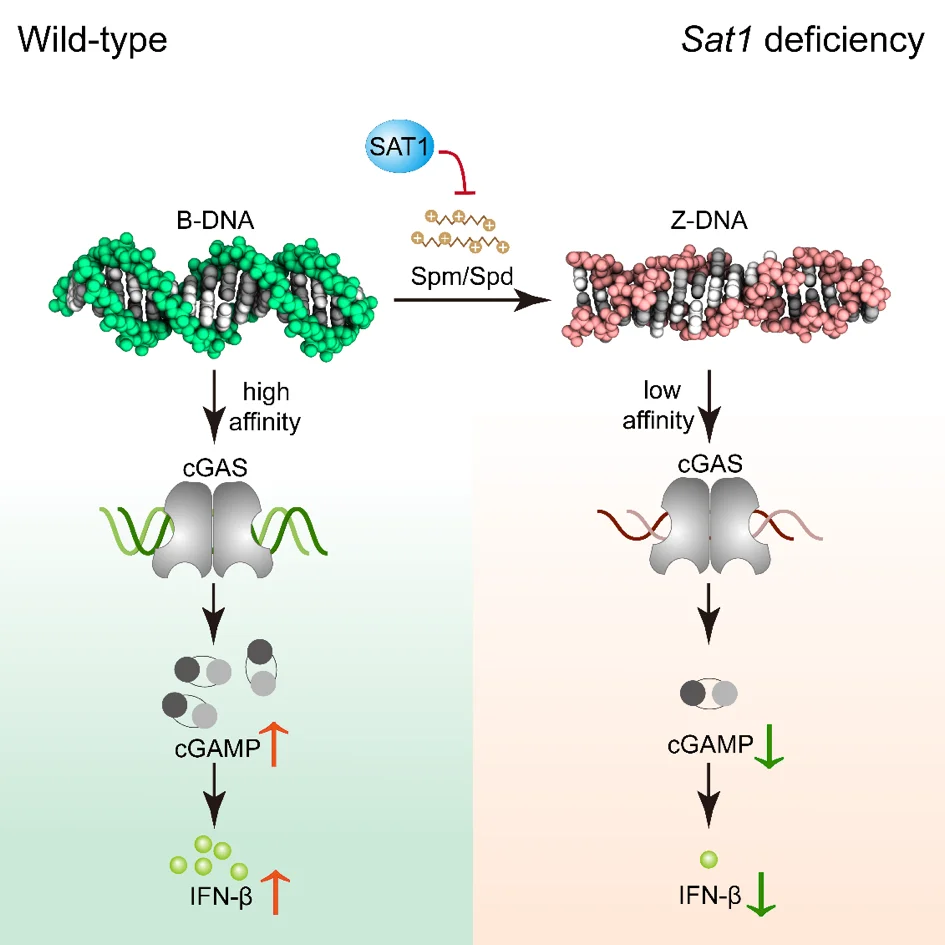
Polyamine metabolism controls B-to-Z DNA transition to orchestrate DNA sensor cGAS activity
to study the regulation mechanism of cGAS activity in order to prevent and treat viral diseases, a research team leading by Prof. Zhao in Shandong University used the HeLa cell line with STING1 gene knockout constructed by Ubigene as the key cell model, and found out that the two conformations of DNA (B-DNA and Z-DNA) had different affinity with cGAS; The endogenous metabolism of small molecules spermine, spermidine and polyamine catabolism key enzyme SAT1 regulates cGAS activity by inducing DNA conformational transition. This research reveals a additional mechanism for preventing abnormal cytoDNA recognition and providing promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of diseases involving improper cGAS activation. View details
View Picture
TP53 Knockout in HCT116 cell line——Apoptosis
IF=16.6
Nature Communications
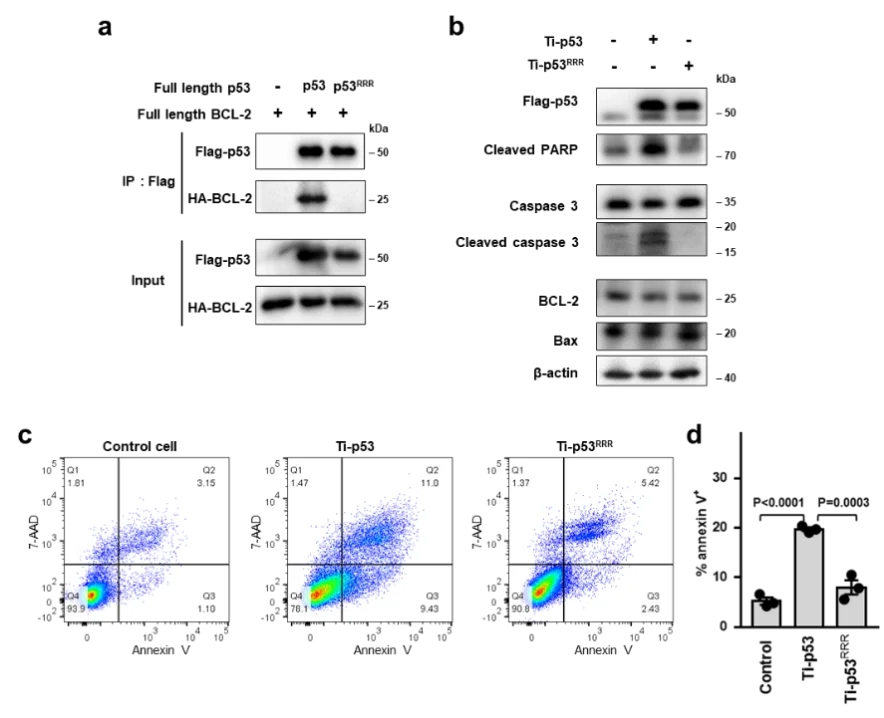
Structures of p53/BCL-2 complex suggest a mechanism for p53 to antagonize BCL-2 activity
In this study, the HCT116 cell line with TP53 gene knocked out constructed by Ubigene was used. By analyzing the crystal structure of the complex of p53 and the anti-apoptotic protein BCL-2, and combining biochemical and cellular experiments, this study revealed a new mechanism of p53 interacting with BCL-2 protein and promoting apoptosis, that is, p53 forms a complex with BCL-2 by directly occupying the BH3-binding pocket of BCL-2, and antagonizes BCL-2 activity by releasing pro-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins located in the pocket, thereby promoting apoptosis.These structural and functional data provide a new idea for further understanding the complex regulatory mechanism of p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis, and also provide an important basis for developing anticancer therapeutic strategies that target protein-protein interactions to activate apoptosis. View details
View Picture
ZNF432 knockout U2OS cell line——Ovarian cancer drug resistance
IF=14.9
Nucleic Acids Research
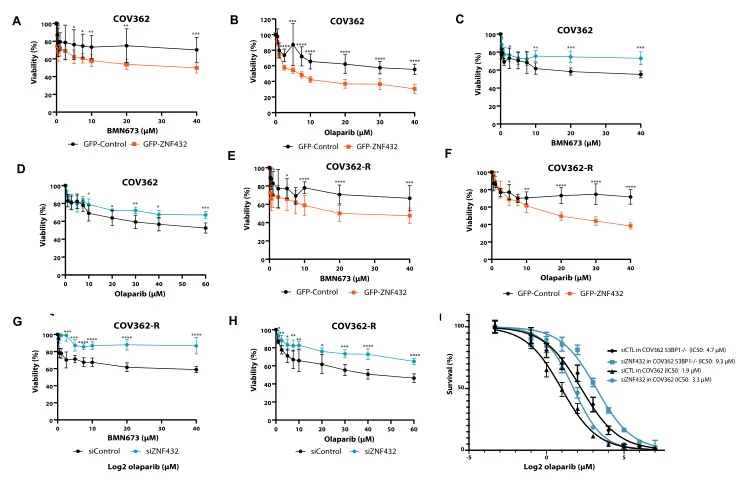
ZNF432 stimulates PARylation and inhibits DNA resection to balance PARPi sensitivity and resistance
ZNF protein was confirmed as a key factor regulating the genome integrity of mammalian cells. In order to explore the possibility that ZFP can be used as an effector of DNA repair based on homologous recombination (HR), Jean Yves Masson team of Laval University used the ZNF432 knockout U2OS cell line constructed by Ubigene to carry out a series of experiments, and found that ZNF432 deletion in cancer cells would accelerate DNA repair, lead to the weakening of PARPi effect, and make ovarian cancer cells develop drug resistance, confirming that ZNF432 is a new HR inhibitor, which successfully broadened the new way to study the efficacy of PARPi. View details
View Picture
SNORD17 Knockout in HepG2 cell line——liver tumors
IF=12.4
Cell death & differentiation
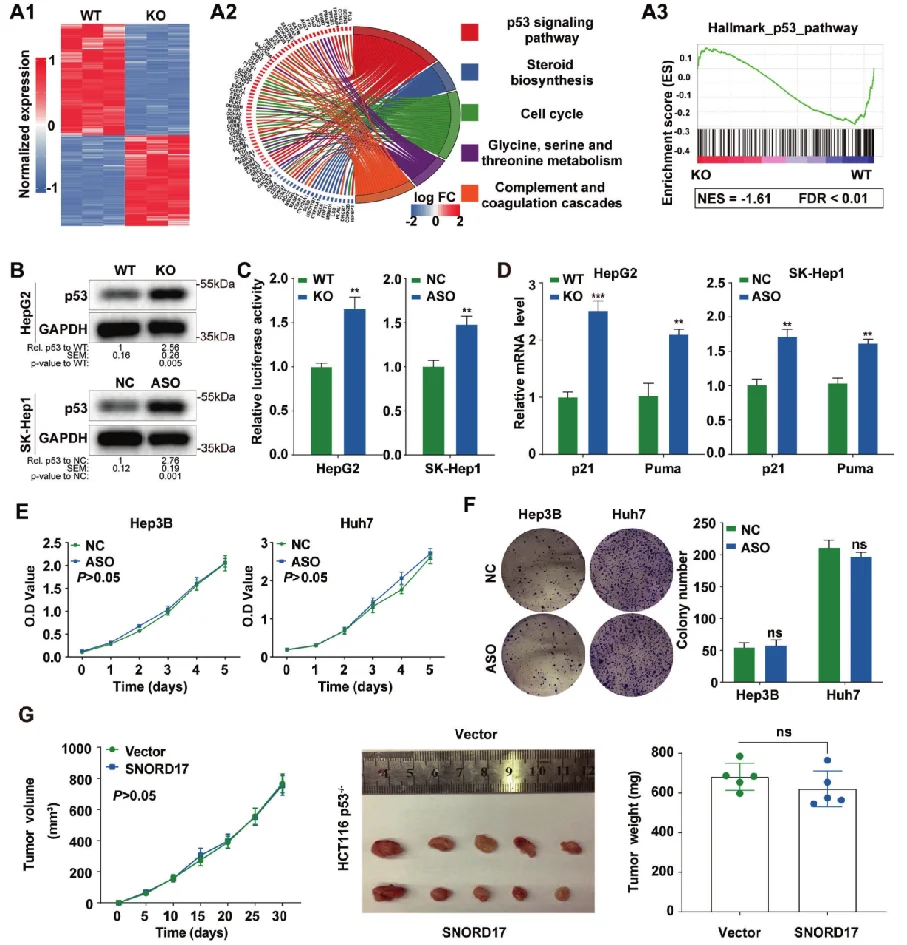
Non-coding small nucleolar RNA SNORD17 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through a positive feedback loop upon p53 inactivation
This study reveals the regulatory role of small nucleolar RNA SNORD17 and p53 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma, which provides a new potential target for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma . The researchers utilized SNORD17 knockout Hep G2 cell line (constructed by Ubigene) as the key cell model. After applied with in vitro and in vivo tests, they found out that in HCC cell lines, the knockout of SNORD17 gene can significantly inhibit cell proliferation, clone formation and G1/S phase transition. View details
View Picture
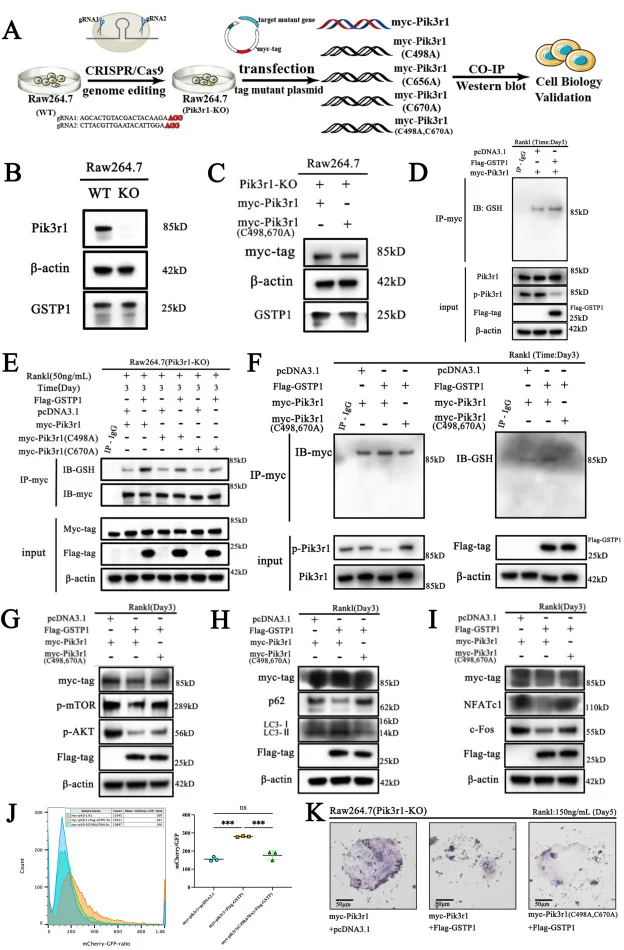
Pik3r1 knockout RAW264.7 cell line - Osteoporosis
IF=11.4
Redox Biology
GSTP1-mediated S-glutathionylation of Pik3r1 is a redox hub that inhibits osteoclastogenesis through regulating autophagic flux
This article explores a new mechanism for GSTP1 affecting the osteoclast cell-related bone homeostasis through combining with a large number of in vivo and in vitro experiments, based on the Pik3r1 knockout RAW264.7 cell model constructed by Ubigene. It was the first time to interpret that the cell fate of osteoclasts is determined by S-glutathionylation via a redox-autophagy which is mediated by GSTP1. View details
View Picture