Location:Home > Application > Bioluminescence Imaging In Vivo: Luciferase Guide
Bioluminescence Imaging In Vivo: Luciferase Guide
Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that utilizes light emitted by living organisms to visualize and measure biological processes in real time. This light emission results from a biochemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme luciferase in the presence of its substrate, luciferin, oxygen, and ATP.
Unlike other imaging modalities, BLI does not require external illumination, reducing background noise and ensuring superior signal specificity. Its ability to detect low-intensity light emissions makes it a highly sensitive method for studying intricate biological phenomena.
BLI’s non-invasive nature allows researchers to perform longitudinal studies, tracking the same subjects over extended periods. This minimizes variability and enhances the reliability of experimental outcomes.
The roots of bioluminescence imaging date back to the discovery of luciferase in fireflies, jellyfish, and other bioluminescent organisms. Over the decades, advances in molecular biology have enabled the integration of luciferase genes into diverse model systems, expanding the technique’s applications in oncology, infectious diseases, and neuroscience.
In this article
BLI’s versatility and precision make it indispensable in modern scientific research. Here are some specific advantages:
Researchers can observe dynamic changes, such as tumor growth or immune cell migration, as they occur. This ability is especially beneficial for studying disease progression and therapeutic effects.
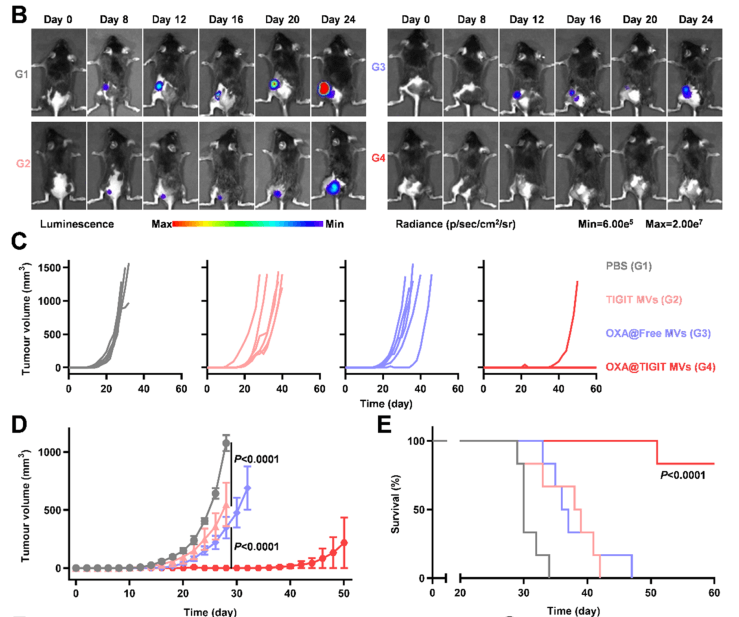
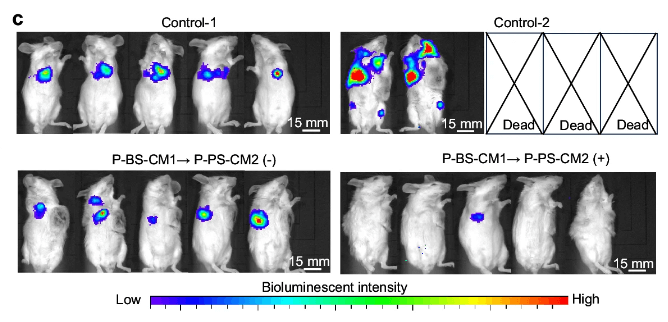
Figure 1. Evaluation of the suppressive effect of re-vaccination on tumor growth
Even subtle changes in cellular activity are detectable due to the high sensitivity of luciferase-based systems. This makes BLI an excellent choice for studying early-stage diseases or low-abundance biomarkers.
The non-invasive nature of BLI reduces the need for euthanizing subjects, aligning with the ethical principles of the 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) in animal research.
For example, in drug discovery, BLI allows pharmaceutical researchers to evaluate drug efficacy in vivo without sacrificing the experimental model. This results in cost savings and more humane research practices.
Luciferase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the reaction that produces bioluminescent light. The process involves the oxidation of luciferin in the presence of oxygen and ATP, yielding photons detectable by specialized cameras.
Luciferase catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin, producing oxyluciferin, light, and other byproducts. The emitted light correlates directly with the biological activity under investigation.
When applied to vivo studies, luciferase genes are introduced into cells or animal models via genetic engineering. Upon administering luciferin, the resulting bioluminescent signal serves as a marker for cellular or molecular activity. This method is widely used to:
The ability to quantify light emissions ensures that BLI provides both qualitative and quantitative data, making it a preferred method in high-throughput drug screening.
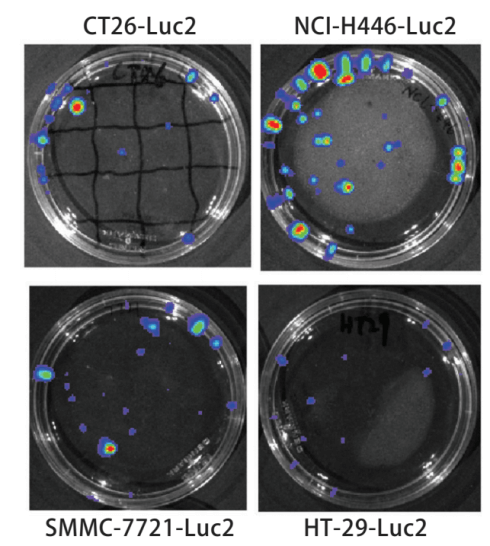
Figure 2. Bioluminescence test for Luc2-positive cell line
Luciferase imaging, as a core tool in bioluminescence research, enables scientists to unravel complex biological phenomena with precision and real-time tracking. Its versatility spans across various research areas, making it a cornerstone of modern experimental science.
Luciferase in vivo imaging is instrumental in oncology for visualizing tumor growth, metastasis, and therapeutic outcomes. Specific applications include:
Example: Researchers using luciferase-labeled glioblastoma cells can visualize tumor regression following CRISPR-mediated gene therapy, providing clear evidence of therapeutic success.
Luciferase imaging enables real-time visualization of infection progression and the efficacy of antimicrobial treatments. Specific examples include:
This application is especially critical in the fight against antibiotic resistance, where rapid and precise evaluation of drug efficacy is crucial.
Luciferase in vivo imaging tracks immune cell behavior, migration, and interaction with diseased tissues. For instance:
Luciferase imaging accelerates drug discovery by offering a robust, non-invasive way to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in vivo.
In regenerative medicine, luciferase imaging tracks stem cell differentiation and tissue repair processes. Applications include:
Luciferase imaging stands out due to its unparalleled sensitivity and ability to integrate seamlessly with genetically engineered models. It is especially advantageous in longitudinal studies, where repeated measurements are essential for understanding dynamic biological processes.
By leveraging high-quality luciferase cell lines like those from Ubigene, researchers can conduct precise, reproducible experiments across these diverse applications.
To achieve accurate and reproducible results in in vivo luciferase imaging, meticulous adherence to protocols is essential.
Choose a luciferase-labeled model (e.g., transgenic mice or engineered cell lines) tailored to your research goals.
Prepare the luciferin substrate according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Use freshly prepared solutions to ensure consistent signal output.
Quantify luminescence signals using imaging software, normalizing against controls to account for variability.
As a trusted leader in genetic engineering, Ubigene provides a diverse portfolio of luciferase-labeled cell lines designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern research.
Explore our Gene-editing series products and services.
Bioluminescence imaging in vivo has become an essential tool for studying biological processes, offering unmatched sensitivity, non-invasiveness, and versatility. Whether monitoring tumor growth, tracking immune cell migration, or evaluating drug efficacy, BLI empowers researchers to gain deeper insights into complex systems.
With Ubigene’s premium luciferase cell lines, researchers can achieve reproducible, high-quality results that drive scientific discovery. Explore our innovative solutions today and unlock the full potential of your research.


Bioluminescence Imaging In Vivo: Luciferase Guide

Bioluminescence imaging (BLI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that utilizes light emitted by living organisms to visualize and measure biological processes in real time. This light emission results from a biochemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme luciferase in the presence of its substrate, luciferin, oxygen, and ATP.
Unlike other imaging modalities, BLI does not require external illumination, reducing background noise and ensuring superior signal specificity. Its ability to detect low-intensity light emissions makes it a highly sensitive method for studying intricate biological phenomena.
BLI’s non-invasive nature allows researchers to perform longitudinal studies, tracking the same subjects over extended periods. This minimizes variability and enhances the reliability of experimental outcomes.
The roots of bioluminescence imaging date back to the discovery of luciferase in fireflies, jellyfish, and other bioluminescent organisms. Over the decades, advances in molecular biology have enabled the integration of luciferase genes into diverse model systems, expanding the technique’s applications in oncology, infectious diseases, and neuroscience.
In this article
BLI’s versatility and precision make it indispensable in modern scientific research. Here are some specific advantages:
Researchers can observe dynamic changes, such as tumor growth or immune cell migration, as they occur. This ability is especially beneficial for studying disease progression and therapeutic effects.

Figure 1. Evaluation of the suppressive effect of re-vaccination on tumor growth
Even subtle changes in cellular activity are detectable due to the high sensitivity of luciferase-based systems. This makes BLI an excellent choice for studying early-stage diseases or low-abundance biomarkers.
The non-invasive nature of BLI reduces the need for euthanizing subjects, aligning with the ethical principles of the 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, Refinement) in animal research.
For example, in drug discovery, BLI allows pharmaceutical researchers to evaluate drug efficacy in vivo without sacrificing the experimental model. This results in cost savings and more humane research practices.
Luciferase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the reaction that produces bioluminescent light. The process involves the oxidation of luciferin in the presence of oxygen and ATP, yielding photons detectable by specialized cameras.
Luciferase catalyzes the oxidation of luciferin, producing oxyluciferin, light, and other byproducts. The emitted light correlates directly with the biological activity under investigation.
When applied to vivo studies, luciferase genes are introduced into cells or animal models via genetic engineering. Upon administering luciferin, the resulting bioluminescent signal serves as a marker for cellular or molecular activity. This method is widely used to:
The ability to quantify light emissions ensures that BLI provides both qualitative and quantitative data, making it a preferred method in high-throughput drug screening.

Figure 2. Bioluminescence test for Luc2-positive cell line
Luciferase imaging, as a core tool in bioluminescence research, enables scientists to unravel complex biological phenomena with precision and real-time tracking. Its versatility spans across various research areas, making it a cornerstone of modern experimental science.
Luciferase in vivo imaging is instrumental in oncology for visualizing tumor growth, metastasis, and therapeutic outcomes. Specific applications include:
Example: Researchers using luciferase-labeled glioblastoma cells can visualize tumor regression following CRISPR-mediated gene therapy, providing clear evidence of therapeutic success.
Luciferase imaging enables real-time visualization of infection progression and the efficacy of antimicrobial treatments. Specific examples include:
This application is especially critical in the fight against antibiotic resistance, where rapid and precise evaluation of drug efficacy is crucial.
Luciferase in vivo imaging tracks immune cell behavior, migration, and interaction with diseased tissues. For instance:
Luciferase imaging accelerates drug discovery by offering a robust, non-invasive way to assess pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in vivo.
In regenerative medicine, luciferase imaging tracks stem cell differentiation and tissue repair processes. Applications include:
Luciferase imaging stands out due to its unparalleled sensitivity and ability to integrate seamlessly with genetically engineered models. It is especially advantageous in longitudinal studies, where repeated measurements are essential for understanding dynamic biological processes.
By leveraging high-quality luciferase cell lines like those from Ubigene, researchers can conduct precise, reproducible experiments across these diverse applications.
To achieve accurate and reproducible results in in vivo luciferase imaging, meticulous adherence to protocols is essential.
Choose a luciferase-labeled model (e.g., transgenic mice or engineered cell lines) tailored to your research goals.
Prepare the luciferin substrate according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Use freshly prepared solutions to ensure consistent signal output.
Quantify luminescence signals using imaging software, normalizing against controls to account for variability.
As a trusted leader in genetic engineering, Ubigene provides a diverse portfolio of luciferase-labeled cell lines designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern research.
Explore our Gene-editing series products and services.

Bioluminescence imaging in vivo has become an essential tool for studying biological processes, offering unmatched sensitivity, non-invasiveness, and versatility. Whether monitoring tumor growth, tracking immune cell migration, or evaluating drug efficacy, BLI empowers researchers to gain deeper insights into complex systems.
With Ubigene’s premium luciferase cell lines, researchers can achieve reproducible, high-quality results that drive scientific discovery. Explore our innovative solutions today and unlock the full potential of your research.


