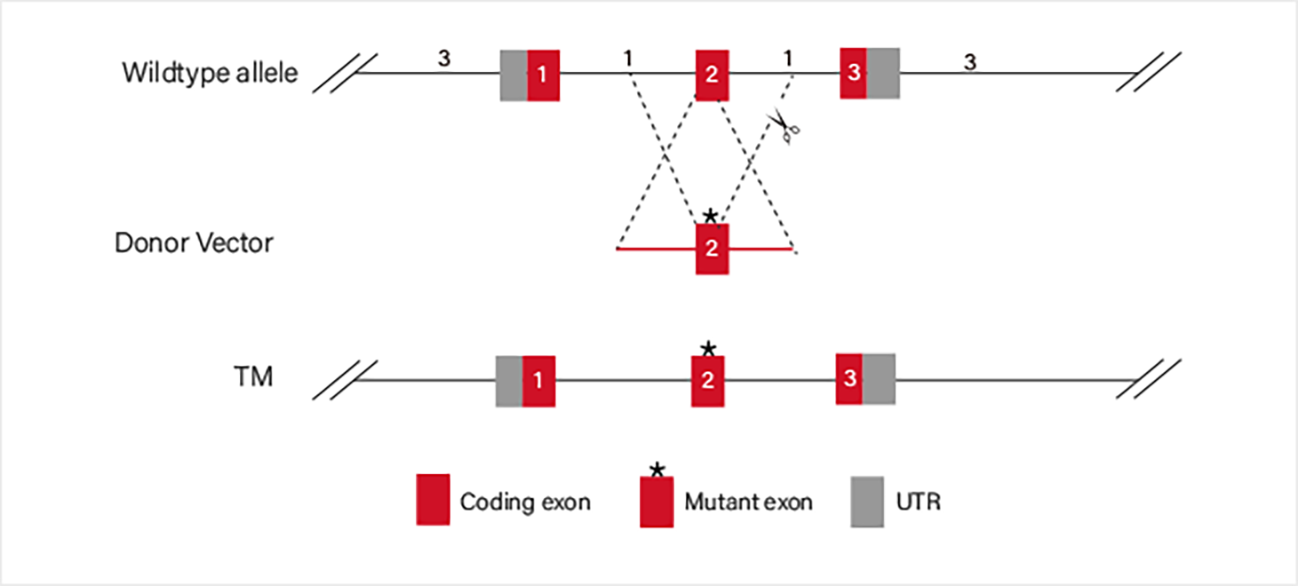
CRISPR-U™ Cell Line
CRISPR-U™ (based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology), developed by
Ubigene, is more efficient than general CRISPR/Cas9 in double-strand breaking, and CRISPR-U™ can greatly improve
the efficiency of homologous recombination, easily achieve
knockout (KO),
point mutation (PM) and
knockin (KI) in vitro and in vivo. With
CRISPR-U, Ubigene has successfully edit genes on more than 100 cell lines.
CRISPR/Cas9 recognizes the target sequence with gRNA, and guide Cas9 endonuclease to cut
the upstream of PAM, resulting in the double-strand break (DSB) of the target site DNA. To repair the DSB, the
cell uses its own DNA repair mechanism to add or delete or replace pieces of DNA sequences via Homology Directed
Repair (HDR) or Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ).
Close CRISPR-U™ (based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology), developed by Ubigene, is more
efficient than general CRISPR/Cas9 in double-strand breaking, and CRI
...show all Digestive System
Digestive SystemHuman colon adenocarcinoma cell line(LS174T)Porcine intestinal epithelial cell line(IPEC-J2)Human hepatoma cell line(HepaRG)Mouse Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line(Hepa 1-6)Mouse Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line(H22)Human Hepatoma Cell Line(SMMC-7721)Human renal carcinoma cell line(ACHN)African green monkey kidney cell(Vero)Human renal cell carcinoma cell line(786-0)Human Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cell Line(KYSE-30)Human Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cell Line(KYSE-150)Human gastric cancer cell line(AGS)Human Gastric Cancer Cell Line(SGC-7901)Human Gastric Cancer Cell Line(HGC-27)Human hepatobiliary cancer cell line(RBE)Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line(HuH-7)Human Hepatoma Cell Line(Hep3B)Human liver cancer cell line(Hep G2)Human Normal Hepatocytes Cell line(L-02)Human colon carcinoma cell line(T84)Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line(Caco-2)Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line(NCI-H716)Human colon adenocarcinoma cell line(DLD-1)Murine colorectal carcinoma cell line(CT26.WT)Murine Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Line(MC38)Human caucasian colon adenocarcinoma cell line(COLO 205)Human colon carcinoma cell line(RKO)Human Colon Cancer Cell Line(HT-29)Human Colon Cancer Cell Line(SW620)Human Colon Cancer Cell Line(SW480)Human Colon Cancer Cell Line(HCT 116)
 Endocrine System
Endocrine SystemHuman Breast Cancer Cell Line(MCF7)Mouse insulinoma β cell line(NIT-1)Human Breast Cancer Cell Line(JIMT-1)Human breast cancer cell line(T-47D)Human pancreatic cancer cell line(BxPC-3)Mouse Acinar Pancreatic Cell Line(266-6)Human Prostate Cancer Cell Line(VCaP)Human Pancreatic Carcinoma Cell Line(MIA PaCa-2)Mouse medullary breast cancer cell line(E0771)Mouse pancreatic cancer cell line(Pan02)Human Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell Line(AsPC-1)Human Breast Adenocarcinoma Cell Line(SK-BR-3)Human Pancreatic Carcinoma Cell Line(PANC-1)Rat Breast Cancer Cell Line(4T1)Human Breast Cancer Cell Line(ZR-75-1)Human Breast Cancer Cell Line(MDA-MB-231)
 Respiratory System
Respiratory SystemChinese hamster lung cells(V79)Human hypopharyngeal carcinoma cell line(FaDu)Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Line(16HBE)Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Line(BEAS-2B)Human Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cell Line(HCC827)Human Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cell Line(NCI-H1299)Human Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line(NCI-H226)Human lung squamous cell carcinoma cell line(SK-MES-1)Human Lung Cancer Cell Line(NCI-H520)Human Lung Cancer Cell Line(Calu-1)Human Lung Cancer Cell Line(A549)
 Blood and Lymphatic System
Blood and Lymphatic SystemHuman B lymphoma cell line(Su-DHL-4)Human B Cell Lymphoma Cancer Cell Line OCI-LY3(OCI-LY3)Human B Cell Lymphoma Cancer Cell Line(U2932)Human Acute Non-B Non-T Lymphocytic Leukemia Cell Line(Reh)Human myelogenous leukemia cell line(K-562)Human T lymphocyte cell line(Jurkat, Clone E6-1)Rat Basophil Leukemia Cell Line(RBL-2H3)Human Monocytic Cell Line(THP-1)Porcine alveolar macrophage cell line(3D4/21)Mouse Macrophage Cell Line(RAW264.7)
 Urinary System
Urinary SystemMouse prostate cancer cell line(RM-1)Rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cell line(PC-12)Distal nephron cell line(Distal nephron cell line(JU4s))Dog Kidney Cell Line(MDCK)Human prostate cancer cell line(22RV1)Human Embryonic Kidney Cell Line(293T)Human Embryonic Kidney Cell Line(HEK293)Human Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma Cell Line(T24)Human bladder carcinoma cell line(5637)Human bladder carcinoma cell line(TCCSUP)
 Reproductive System
Reproductive SystemHuman ovarian cancer cell line(OVCAR-3)Human Villous Trophoblast(HTR-8/SVneo)Human Ovarian Adenocarcinoma Cell Line(CAOV3)Mouse Testicular Stromal Cell Line(TM3)Mouse Pituitary Cell Line(Lbetat2)Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Line(SK-OV-3)Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Line(CHO-K1)Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts(NIH/3T3)Human Cervical Carcinoma Cell Line(HeLa 229)Human Cervical Carcinoma Cell Line(HeLa)
 Circulatory System
Circulatory SystemMouse Myoblast Cell Line(C2C12)Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cell line(HCAEC)Rat Cardiac Myocytes(HL-1)Rat Cardiac Myocytes(H9C2)
 Brain and Nervous System
Brain and Nervous SystemHuman glioma cell line(U251MG)Mouse microglia cell line(BV2)Immortalize Human Microvascular Endothelial Cell Line(hCMEC/D3)Mouse Anterior Parietal Bone Cell Line(MC3T3-E1 Subclone 14)Human glioblastoma cell line(U-87 MG)Rat Glioblastoma Cell Line(C6)Mouse neuroblastoma cell line(Neuro-2a)Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line(SK-N-SH)
 Skeleton, Articulus, Soft Tissue, Derma System
Skeleton, Articulus, Soft Tissue, Derma SystemMouse osteoid cell line(MLO-Y4)Ameloblastoma(hTERT-AM)Mouse squamous carcinoma cell line(SCC7)Mouse myeloma cell line(Sp2/0-Ag14)Human skin squamous carcinoma cell line(A431)Murine melanoma cell line(B16-F10)Human Melanoma Cell Line(M14)Human malignant melanoma cell line(A-375)Human fibrosarcoma cell line(HT-1080)Human bone osteosarcoma epithelial cell line(U-2 OS)Human Osteosarcoma Cell Line(MG-63)
 Ocular, Otolaryngologic and Oral System
Ocular, Otolaryngologic and Oral SystemHuman retinal pigment epithelial cell line(ARPE-19)Human choroidal melanoma cell line(OCM-1)Human oral squamous carcinoma cell line(HSC3)Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cell Line(C666-1)Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cell Line(CNE2Z)Human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line(NPC-43)Rat Muller Cell Line(rmc-1)
 Stem Cell
Stem CellStem Cell(H9)Human Embryonic Stem Cell(H1)Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell(ipsc)
Technical advantage
Exclusive innovation, 10 times more efficient in gene-editing.
Successfully edit genes on more than 100 types of cell lines.
Easily generate knockout (KO), point mutation (PM) and knockin (KI) in vitro and in vivo.
CRISPR-U™ offers a 100% mutation guarantee. No mutation, no charge!
Point Mutation Cell
Lines
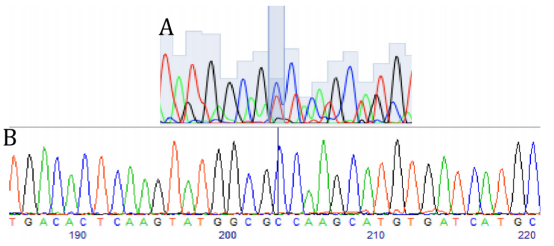
CRISPR/Cas9 and ssODN used to repair the point mutation in A79V-hiPSC. A) Genomic sequence
surrounding the mutation site: mutated nucleotide (T, red); sgRNA recognition site containing 20 bp (yellow);
CRISPR cutting site between the 17th and 18th bp (bold); forward and reverse primers (pink). B) ssODN with 120 bp,
60 bp upstream and 60 bp downstream the mutation site containing the WT nucleotide (C, green).
Point mutation Strategy
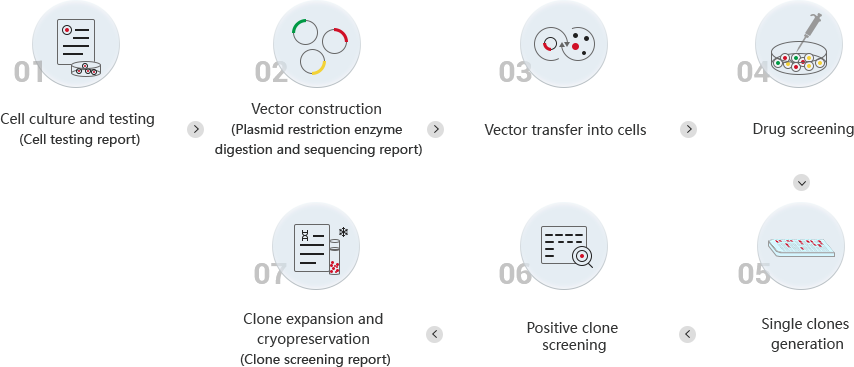
Work Flow and Validation
Case Study
The A79V mutation of PSEN1 gene can cause Alzheimer's disease. Somatic cells of patients with
Alzheimer's disease are induced into pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and then the mutant gene is modified by
replacing the point mutation with a wild-type sequence. By studying the iPSC of patients and the modified iPSC, we
can know the effect of the mutation on cell phenotype, so as to further study the pathological effect of the
mutation.
CRISPR/Cas9 and ssODN used to repair the point mutation in A79V-hiPSC.
A) Genomic
sequence surrounding the mutation site: mutated nucleotide (T, red); sgRNA recognition site containing 20 bp
(yellow); CRISPR cutting site between the 17th and 18th bp (bold); forward and reverse primers (pink).
B)
ssODN with 120 bp, 60 bp upstream and 60 bp downstream the mutation site containing the WT nucleotide (C,
green).
B. Sequencing of exon 4 of the PSEN1 gene in hiPSCs.
A) Heterozygous c.236C>T
substitution in the mother line previously published.
B) Successful correction of the point mutation
(T>C).
Reference:
Fukuda, N., Senga, Y., & Honda, S. (2019). Anxa2‐and Ctsd‐knockout CHO cell lines to
diminish the risk of contamination
with host cell proteins. Biotechnology progress, e2820.