Cell Apoptosis
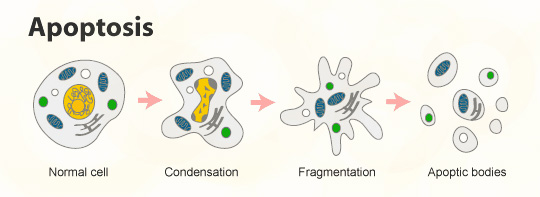
Apoptosis refers to the orderly, autonomous death of cells controlled by genes to maintain the homeostasis. Apoptosis, unlike necrosis, is not a passive process, but an active one, which involves the activation, expression, and regulation of a series of genes, etc. Apoptosis is not a phenomenon of autophagic injury under pathological conditions, but rather a death process actively strived for better adaptation to the living environment.
Apoptosis is a tightly controlled process of multiple genes.These genes are well conserved among species, such as Bcl-2 family, Caspase family, oncogenes such as C-myc, tumor suppressor p53 and so on. With the development of molecular biological techniques, there has been considerable understanding of the process of apoptosis in a variety of cells, but to date the exact mechanism of the apoptotic process is not fully understood. Disturbance of the apoptotic process may have a direct or indirect relationship with the occurrence of many diseases, such as tumors and autoimmune diseases, etc., and many factors can induce apoptosis, such as radiation, drugs, etc.
Technical details
Principle of cell apoptosis detection by Annexin V/PI double staining:
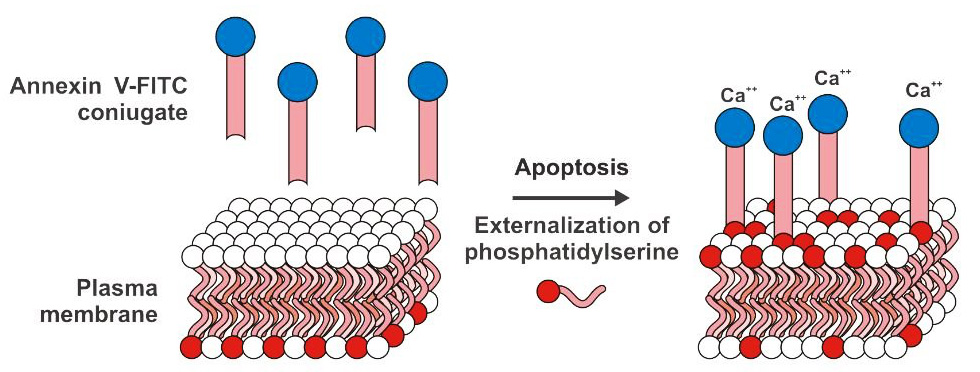
Phosphatidylserine (PS) is normally located on the inner side of the cell membrane, but in the early stage of apoptosis, PS flips from the inner side of the cell membrane to the surface of the cell membrane to be exposed in extra-cellular circumstance. Annexin-V is a Ca2+ dependent phospholipid binding protein with molecular weight ranging from 35 to 36 KD, which can specifically bind to PS with high affinity.
Propidium (PI) is a fluorescent dye for double stranded DNA. Upon binding of PI and double stranded DNA, it can produce fluorescence, and the fluorescence intensity and the content of double stranded DNA are directly proportional. After the intracellular DNA is stained by PI, the cells can be used to determine the DNA content by flow cytometry. Then, according to the distribution of DNA content, cell cycle and apoptosis analysis are performed. After PI staining, assuming a fluorescence intensity of 1 for cells in G0 / G1 phase, the theoretical value of the fluorescence intensity of G2 / M phase cells is 2 containing duplicate copies of genomic DNA, and that of S phase cells undergoing DNA replication is between 1-2. Apoptotic cells that undergo condensation of nuclei as well as DNA fragmentation results in the loss of part of the genomic DNA fragment during staining, so that apoptotic cells display a distinct weak staining after PI staining, ie, fluorescence intensity less than 1, with the sub-G1 peak on fluorescent image of flow cytometry detection.
When cells undergo apoptosis, the light scattering properties of the cell change due to cytosolic and chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation, and generation of apoptotic bodies. At the early stage of apoptosis, the ability of cells to respond to forward angle light scattering is significantly reduced and their ability to respond to side light scattering is increased or unchanged. In the late stage of apoptosis, signals of both forward and side light scatter are decreased. Therefore, the apoptosis could be observed of the changes in light scattering of the cells by flow cytometry assay.
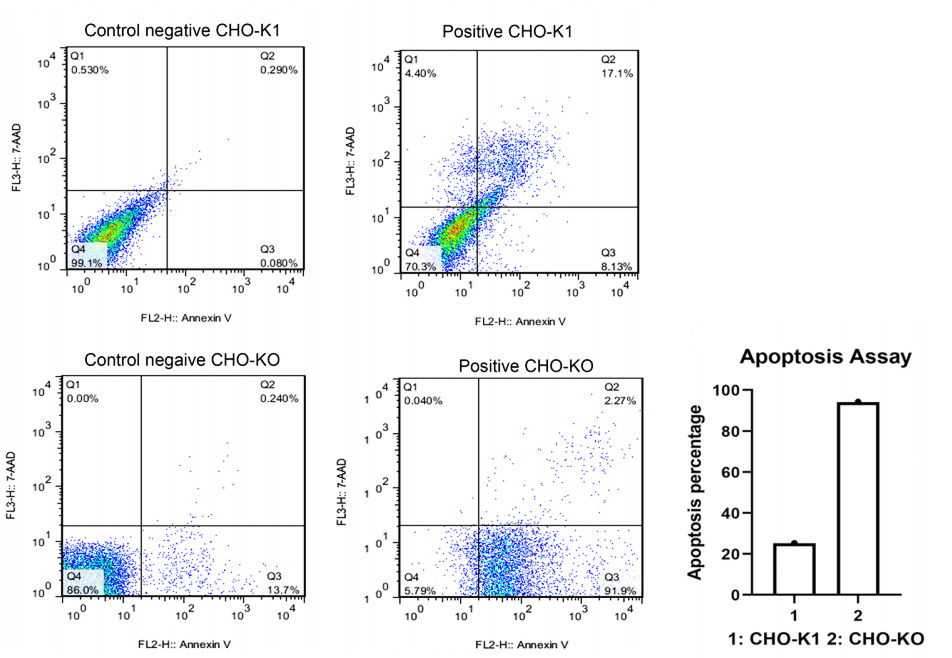
Case study
Reference
Safari, Fatemeh et al. “Caspase-7 deficiency in Chinese hamster ovary cells reduces cell proliferation and viability.” Biological research vol. 53,1 52. 13 Nov. 2020, doi:10.1186/s40659-020-00319-x
Service turnaround and deliverables

Service turnaround
5~10 business days, depending on cell growth and experimental design

Customer provides
cell lines, drugs, drug treatments and experimental conditions parameter settings

Deliverables
raw data, analytical results, experimental reports
Other method to detect cell apoptosis
| Principle | Features |
|---|
| TUNEL assay | The 3 '- OH end of a series of DNAs generated by DNA double strand breaks or by nicking on only one strand can be labeled by a derivative formed by deoxyribonucleotides and fluorescein, peroxidase, alkaline phosphorylase, or biotin, under the action of Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT). Thereby the detection of apoptotic cells can be performed, and this type of method generally refers to the deoxyribonucleotide terminal transferase mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) method. | It can accurately reflect the most typical biochemical and morphological features of apoptosis and can be used for apoptosis assays on paraffin-embedded tissue sections, frozen tissue sections, cultured cells, and cells isolated from tissues. And it can detect very few apoptotic cells. |
| Caspase 3 activity assay | Caspase-3 activation plays an important role in the initiation of cellular events in the apoptotic process, utilizing the principle of fluorometric immunosorbent enzyme assay (FIENA), caspase-3 will act on its specific substrates upon activation. | This method can be used for apoptosis induction studies in a variety of cultured cells and is highly sensitive and specific (specific to anti-caspase-3 mAb) without cross reactivity with other known caspases. |